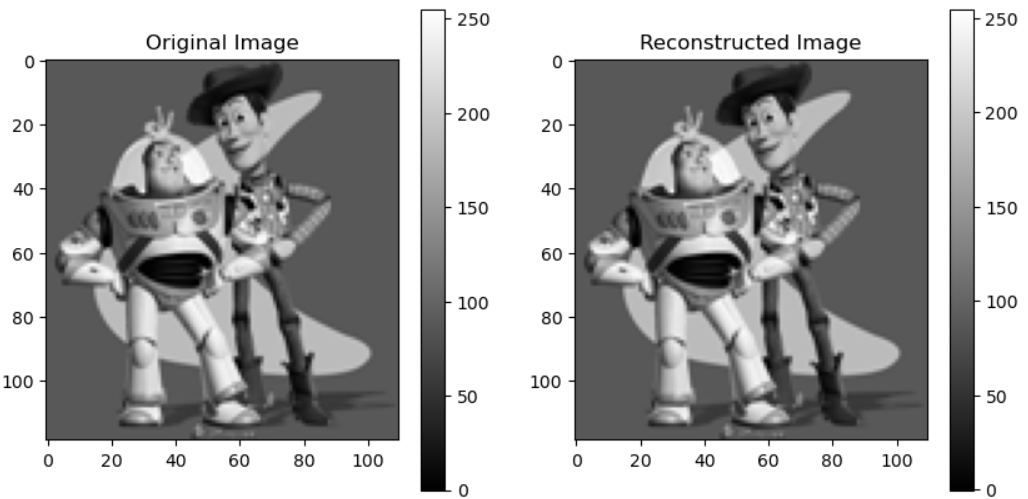
Gradient Domain Processing Example
This example demonstrates gradient domain processing, where an image is reconstructed using its gradients. The process involves:
- Computing the x and y gradients from the source image.
- Using these gradients, along with a fixed pixel intensity constraint, to solve for the output image.
- Reconstructing the image by solving a least squares optimization problem.
Introduction to Poisson Blending
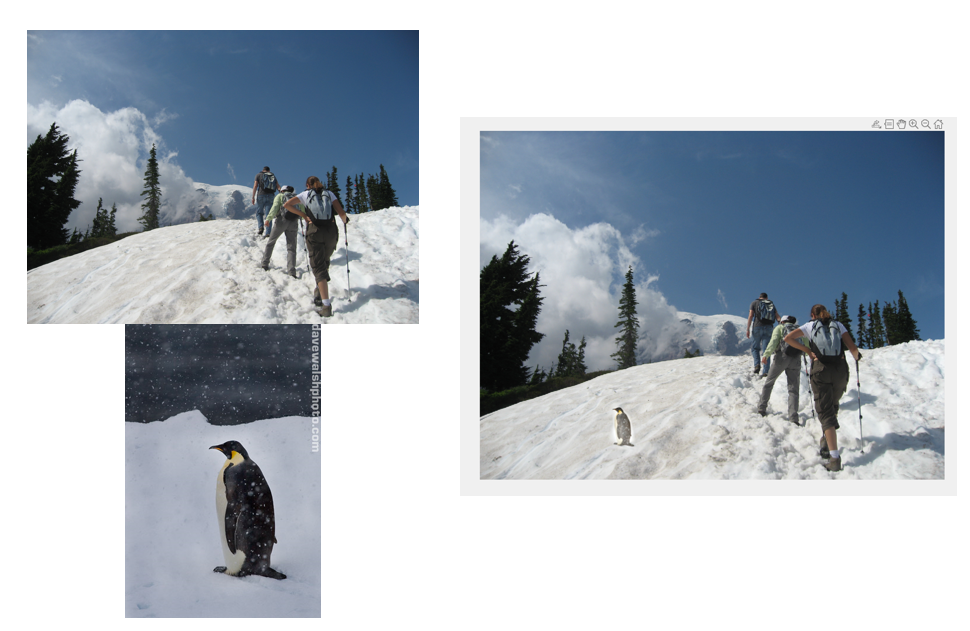
Poisson blending is a specific application of gradient domain processing used for seamless image compositing. The technique solves the Poisson equation to combine parts of a source image into a target image.
It works by:
- Minimizing the difference in gradients between the source and target images within a defined region.
- Ensuring smooth transitions at the boundary by constraining the pixel values to match the target image.
The result is a blended image where the inserted region seamlessly integrates with the background, maintaining consistent lighting and texture. Poisson blending is widely used in image editing tools
for tasks like object insertion, removal, and texture replacement.
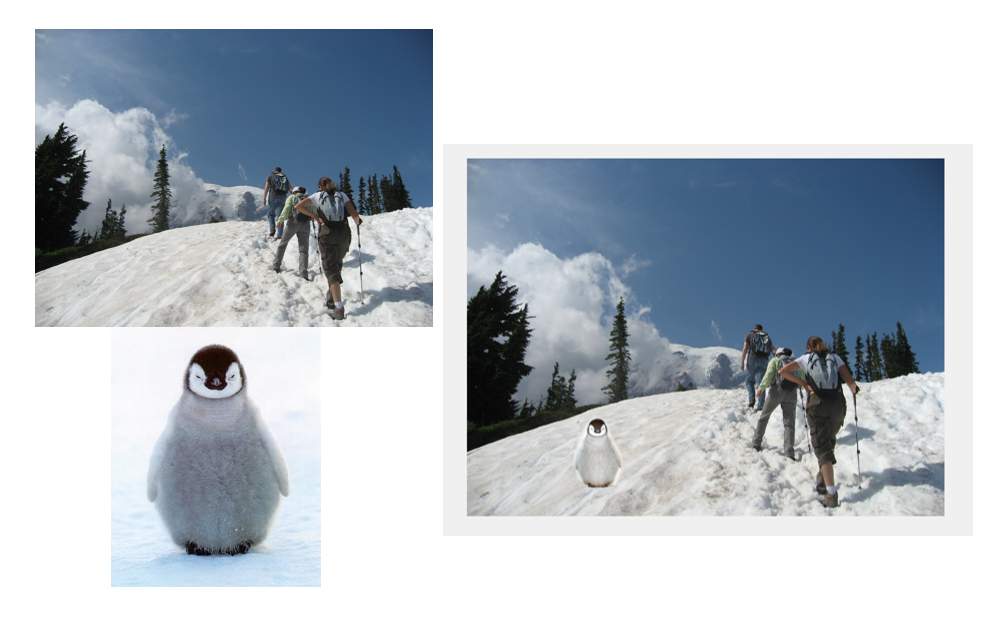
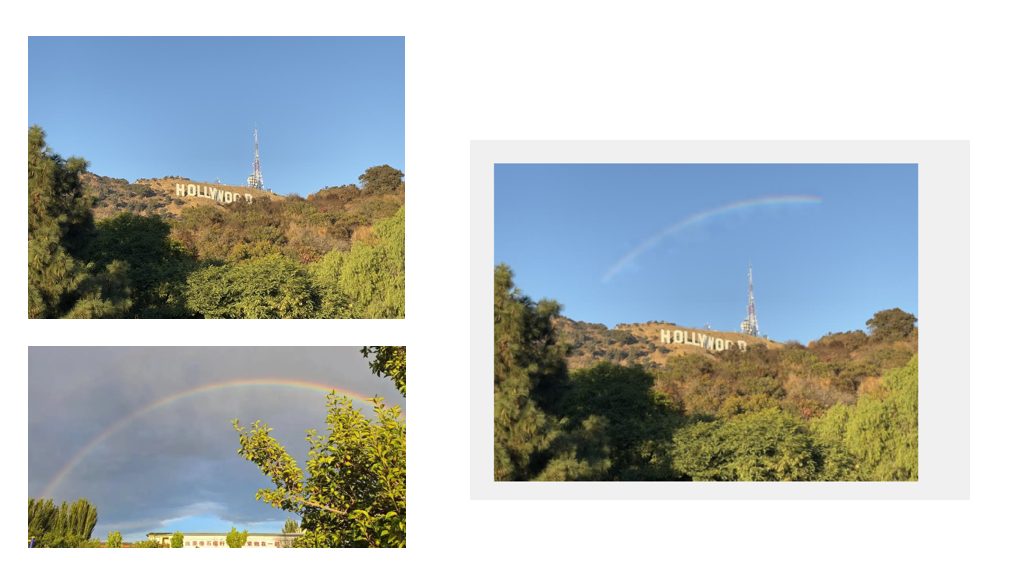



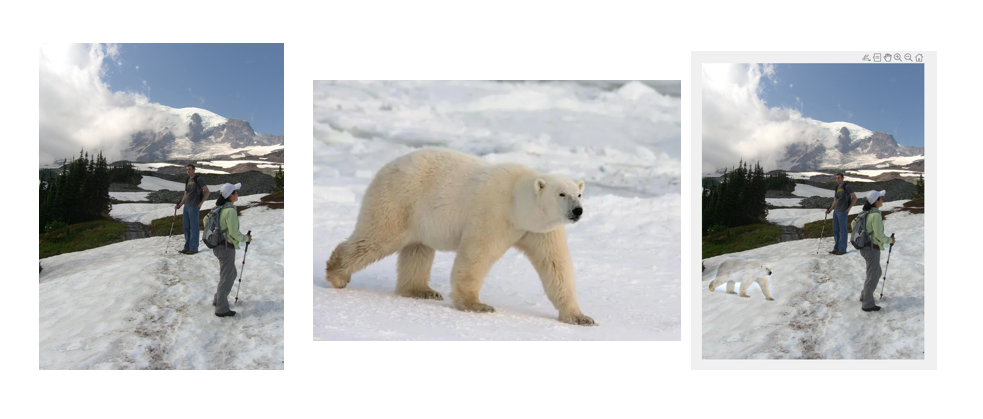
Introduction to Mixed Gradients Blending (Bell and Whistle)
Mixed Gradients Blending is an advanced extension of Poisson blending, designed to achieve more realistic and visually appealing results by combining gradients from both the source and the target images. The key steps include:
- Compute the x and y gradients for both the source and target images in the blending region.
- Select the larger gradient magnitude for each direction (horizontal and vertical) from either the source or target image. This ensures that strong edges or texture details from both images are preserved.
- Calculate the divergence of the selected mixed gradients to form a Laplacian, which guides the reconstruction of the blended image.
- Iteratively solve for the pixel intensities in the blending region by minimizing the difference between neighboring pixels while respecting the computed Laplacian.
By leveraging mixed gradients, this method ensures seamless blending while retaining important features from both images, such as texture, edges, and intensity transitions.







